 In October 2008, I have started an ambitious series of posts on this blog called – Spreadcheats. These are little tricks, nuggets, tutorials on using Excel that would make anyone a spreadsheet guru.
In October 2008, I have started an ambitious series of posts on this blog called – Spreadcheats. These are little tricks, nuggets, tutorials on using Excel that would make anyone a spreadsheet guru.
The spreadcheats series has been wildly successful. I am compiling all this useful information and articles in to one big post so that anyone can follow the links and become good in Excel. Read on,
[Note: This is not for beginners. If you know what a formula is, you would enjoy this 31 articles]
1: Insert Line Breaks in a Cell
Press ALT+Enter keys in a cell to make a new line inside the cell. [Read this]
2: Select all cells in a range
Use these keyboard shortcuts to select all the cells in a range or group. You can find 90 more shortcuts on that page. [Read this]
3: Using Mouse in Excel

Many of us know at few keyboard shortcuts. But what about mouse short-cuts? Read this post to learn interesting mouse shortcuts that can boost your productivity. [Read this]
4: Using Mouse in Excel – Part 2
In the second part of Mouse shortcuts, we explore double click tricks in Excel. [Read this]
5: Save time by using chart templates
In this spreadcheat, learn how to make your own chart templates and re-use them to save time. [Read this]
6: Make ToC (Table of Contents) in Excel – and other tricks
We all run in to large excel workbooks one time or other. Read this post to find out how you can manage when you have a large file. [Read this]
7: How to print spreadsheets one just one page?
Use the little trick in print settings to print any worksheet on just one page. [Read this]
8: Write better formulas by knowing the difference between relative and absolute references

Quick, what is the difference between A1 and $A$1? If you said 2 dollars, you are the right person to read this article. Learning the differences and usages of various reference types in Excel is important if you want to write better and simpler formulas. [Read this]
9: Remove duplicate items using formulas
Learn how to remove duplicates, identify unique values etc. using formulas in this article. [Read this]
10: Introduction to VLOOKUP Formula (and MATCH, OFFSET Formulas)
VLOOKUP remains one of the most important and very useful formulas in Excel. Learn how to write vlookup formulas by reading this article. [Read this]
11: Introduction to 3D References in Excel (a tutorial on Employee Satisfaction Surveys in Excel)
In this tutorial, we will explore a feature called 3D References in Excel and build an employee satisfaction survey form in Excel. [Read this]
12: Introduction to SUMPRODUCT formula
Learn how to use SUMPRODUCT to find sum of values that meet more than one condition. [Read this]
13: Introduction to ROWS and COLUMNS formulas
One of my recent favorites, ROWS() formula is very useful to generate sequential numbers in Excel. [Read this]
14: Calculate Moving Average in Excel
Use excel formulas and relative references to calculate moving average from your data. [Read this]
15: Introduction to FREQUENCY formula
We use FREQUENCY formula in Excel to generate statistical distribution of a set of values in this example. [Read this]
16: How to understand and fix excel formula errors
If you are ever perplexed by #N/A, #NAME! and said #$#@ to excel, this is the article for you. Read it to learn what these errors actually mean and how to fix them. [Read this]
17: Quick tip to Debug Complex Excel Formulas
Use Function key F9 to debug lengthy and complex excel formulas. Select a portion of the formula and press F9 to instantly evaluate that portion and see the result. Read this article to find out how to use this trick. [Read this]
18: Use Find / Replace tool to change formulas
Learn how to use Find / Replace tool in Excel to quickly edit formulas and change them. [Read this]
19: Introduction to COUNTIF and SUMIF Formulas
COUNTIF and SUMIF are very simple yet very powerful formula tools for anyone using Excel. In this article, explore these formulas and learn to use them. [Read this]
20: Introduction to Array Formulas in Excel
Array formula is like a mega formula that would work on an entire range of cells and return another range of cells. They are useful for scenarios where the output we need is not one value but a set of values. In this introductory example, learn how to write your first array formula. [Read this]
21: Introduction to Excel Conditional Formatting
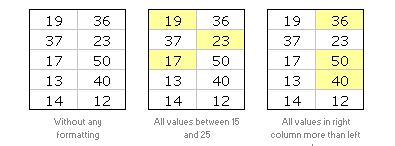
Excel conditional formatting is your way of telling excel to highlight / change formatting of cells that meet certain criteria. This is a good way to draw attention to few points from a large table. Learn how to use Excel CF in this introductory article. [Read this]
22: Introduction to Excel Camera Tool
In this article, learn about Excel Camera (or Snapshot) tool which is useful for making a live snapshot of a range of cells. [Read this]
23: Introduction to Excel Pivot Tables
Pivot tables are a powerful way to analyze and report your data. In this introductory post, you will find all the basics of pivot tables and learn some tricks. [Read this]
24: Introduction to Excel Goal Seek
Goal Seek is opposite of formulas. In formulas we tell excel a bunch of values and excel finds the result. In goal seek, we tell excel what the result should and excel tells us what kind of parameters should be given. This is useful to find, for eg. Your retirement nest egg value … [Read this]
25: Introduction to Combination Charts in Excel
Learn how to combine 2 different chart types in to one chart in this article. [Read this]
26: Make a Dynamic / Interactive Chart using Data Filters
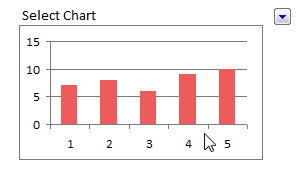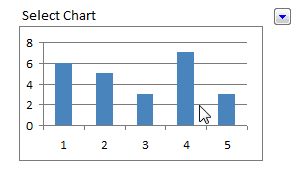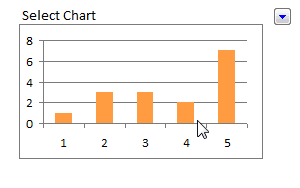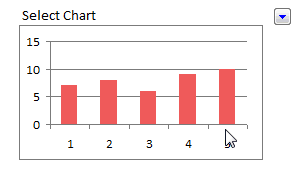
Do you know that we can use data filters to filter charts as well as data? Well, in this article, you can learn a powerful yet simple trick to make a dynamic chart in Excel using data filters alone. [Read this]
27: Make a Dynamic / Interactive Chart using INDEX Formula
Learn how to set up a dynamic or interactive chart using INDEX formula and Camera tool in Excel. [Read this]
28: Make Collapsible Charts using Group – Outline Tools
We can collapse / expand charts using the group and outline tools in Excel. Learn how to set up such a collapsible chart in Excel. [Read this]
29: Showing Chart Labels in Different Colors – Charting Tricks
Learn how to use custom cell formatting codes to show chart labels in different colors based on a criteria. [Read this]
30: Advanced Data Validation Tricks in Excel – Part 1
In part 1 of excel data validation tricks, we will learn how to use excel formulas to control the way data validation works. [Read this]
31: Advanced Data Validation Tricks in Excel – Part 2
In part 2 of data validation tricks, we will learn how to prevent duplicate data entry using data validation formulas. [Read this]
Happy learning 🙂



















8 Responses to “Pivot Tables from large data-sets – 5 examples”
Do you have links to any sites that can provide free, large, test data sets. Both large in diversity and large in total number of rows.
Good question Ron. I suggest checking out kaggle.com, data.world or create your own with randbetween(). You can also get a complex business data-set from Microsoft Power BI website. It is contoso retail data.
Hi Chandoo,
I work with large data sets all the time (80-200MB files with 100Ks of rows and 20-40 columns) and I've taken a few steps to reduce the size (20-60MB) so they can better shared and work more quickly. These steps include: creating custom calculations in the pivot instead of having additional data columns, deleting the data tab and saving as an xlsb. I've even tried indexmatch instead of vlookup--although I'm not sure that saved much. Are there any other tricks to further reduce the file size? thanks, Steve
Hi Steve,
Good tips on how to reduce the file size and / or process time. Another thing I would definitely try is to use Data Model to load the data rather than keep it in the file. You would be,
1. connect to source data file thru Power Query
2. filter away any columns / rows that are not needed
3. load the data to model
4. make pivots from it
This would reduce the file size while providing all the answers you need.
Give it a try. See this video for some help - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5u7bpysO3FQ
Normally when Excel processes data it utilizes all four cores on a processor. Is it true that Excel reduces to only using two cores When calculating tables? Same issue if there were two cores present, it would reduce to one in a table?
I ask because, I have personally noticed when i use tables the data is much slower than if I would have filtered it. I like tables for obvious reasons when working with datasets. Is this true.
John:
I don't know if it is true that Excel Table processing only uses 2 threads/cores, but it is entirely possible. The program has to be enabled to handle multiple parallel threads. Excel Lists/Tables were added long ago, at a time when 2 processes was a reasonable upper limit. And, it could be that there simply is no way to program table processing to use more than 2 threads at a time...
When I've got a large data set, I will set my Excel priority to High thru Task Manager to allow it to use more available processing. Never use RealTime priority or you're completely locked up until Excel finishes.
That is a good tip Jen...