We can take any Excel workbook and format it until Christmas, and we would still not be done. But not many of us have so much of time or energy. So, today, lets talk Excel formatting Tips.

1. Use tables to format data quickly
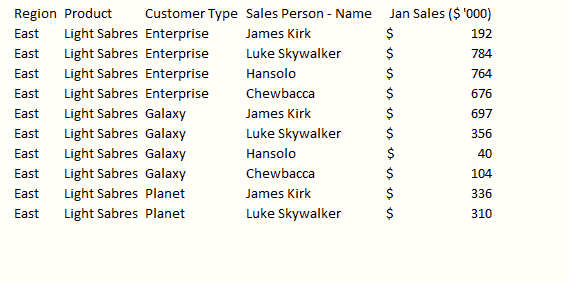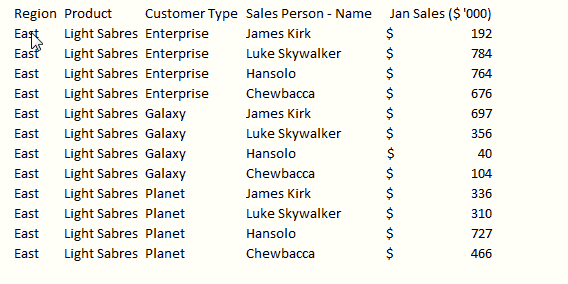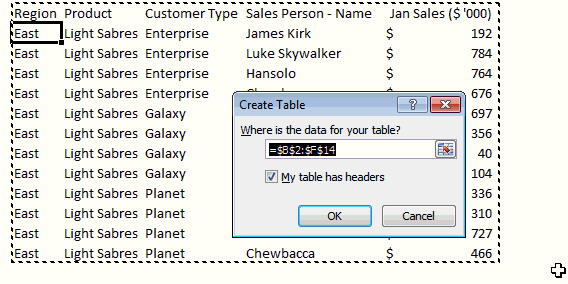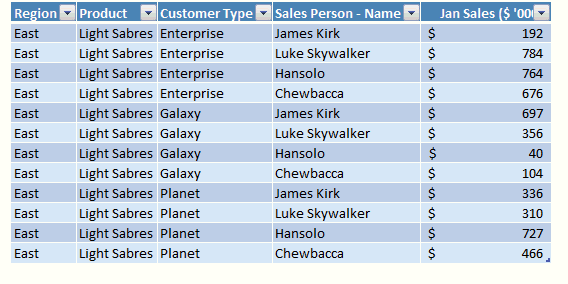
Excel Tables are an incredibly powerful way to handle a bunch of related data. Just select any cell with in the data and press CTRL+T and then Enter. And bingo, your data looks slick in no time. This has to be the best and easiest formatting tip.
Learn more about Excel Tables.
2. Change colors in a snap
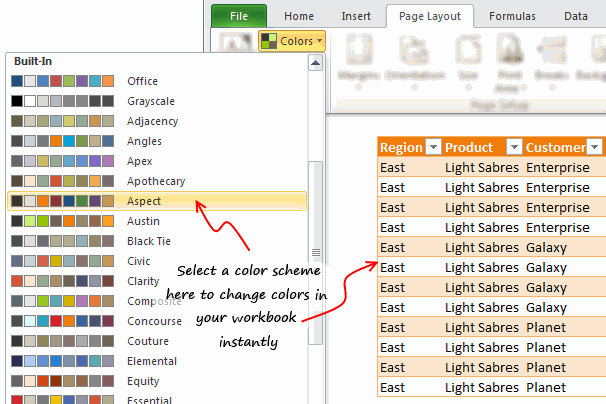
So you have made a spreadsheet model or dashboard. And you want to change colors to something fresh. Just go to Page Layout ribbon and choose a color scheme from Colors box on top left. Microsoft has defined some great color schemes. These are well contrasted and look great on your screen. You can also define your own color schemes (to match corporate style). What more, you can even define schemes for fonts or combine both and create a new theme.
3. Use cell styles
Consistency is an important aspect of formatting. By using cell styles, you can ensure that all similar information in your workbook is formatted in the same way. For example, you can color all input cells in orange color, all notes in light gray etc.
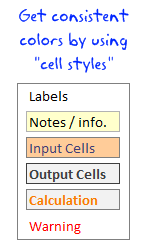
To apply cell styles, just select all the cells you want to have same style and from Home ribbon, select the style you want (from styles area).
Learn how to use cell styles in Excel.
4. Use format painter
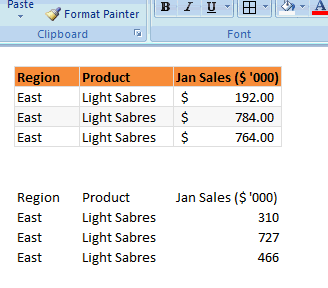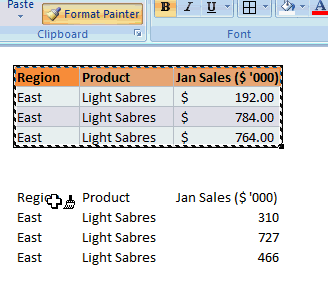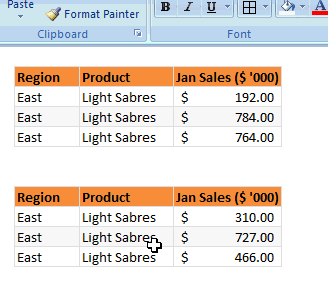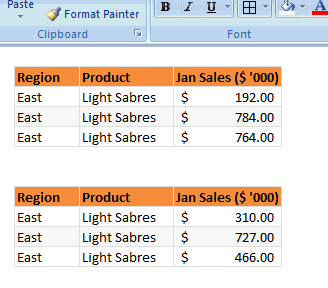
Format painter is a beautiful tool part of all Office programs. You can use this to copy formatting from one area to another. See below demo to understand how this works. You can locate format painter in the Home ribbon, top left.
5. Clear formats in a click
Sometimes, you just want to start with a clean slate. May be it is that colleague down the aisle who made an ugly mess of the quarterly budget spreadsheet. (Hey, its a good idea to tell him about Chandoo.org) So where would you start?
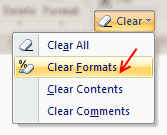
Simple, just select all the cells, and go to Home > Clear > Clear Formats. And you will have only values left, so that you can format everything the way you want.
6. Formatting keyboard shortcuts
Formatting is an everyday activity. We do it while writing an email, making a workbook, preparing a report, putting together a deck of slides or drawing something. Even as I am writing this post, I am formatting it. So knowing a couple of formatting shortcuts can improve your productivity. I use these almost every time I work in Excel.
- CTRL + 1: Opens format dialog for anything you have selected (cells, charts, drawing shapes etc.)
- CTRL + B, I, U: To Bold, Italicize or Underline any given text.
- ALT+Enter: While editing a cell, you can use this to add a new line. If you want a new line as part of formula outcome, use CHAR(10), and make sure you have enabled word-wrap.
- ALT+EST: Used to paste formats. Works like format painter (#4)
- CTRL+T: Applies table formatting to current region of cells
- CTRL+5: To
strike thru. - F4: Repeat last action. For example, you could apply bold formatting to a cell, select another and hit F4 to do the same.
More: Formatting shortcuts for keyboard junkies
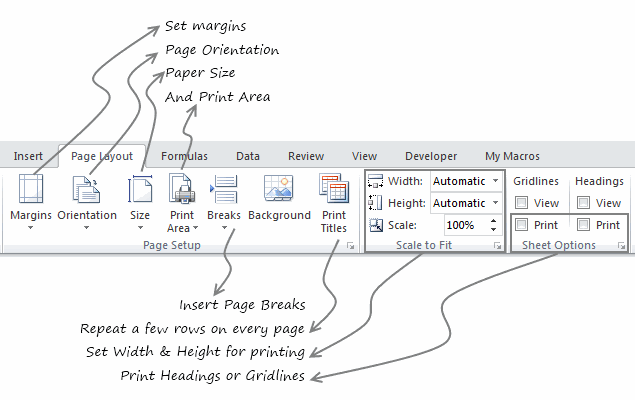
7. Formatting options for print
What looks great on your screen might look messed up, if you do not set correct print options. That is why, make sure that you know how to use these print settings. All of these can be accessed from Page Layout ribbon. For more, you can also use print preview and then “page settings” button.
8. Do not go overboard
Formatting your workbook is much like garnishing your food. No amount of plating & garnishing is going to make your food taste good. I personally spend 80% of time making the spreadsheet and 20% of time formatting it. By learning how to use various formatting features in Excel & relying on productive ideas like tables, cell styles, format painter & keyboard shortcuts, you can save a lot of time. Time you can use to make better, more awesome spreadsheets.
10 Formatting Tricks only Excel experts would know
In addition to the above 8 formatting tips, I made a video explaining more tips. Watch it to learn 10 super cool, secret format tricks to take your spreadsheet game to next level.
- Merging without merging – centre across selection
- Merge multiple cells with “Merge across”
- No decimal points for large numbers with Custom cell formatting
- Showing numbers in Thousands or millions with Custom cell formatting
- New line in a cell with ALT+Enter
- Copy widths alone with paste special
- Skip zero in chart labels with custom cell formatting
- Align & distribute charts with alignment tools
- Show total hours with [h]:mm custom code
- Text format for very long numbers
What are your favorite Excel formatting tips?
Formatting (or making something look good) helps you get great first impression. I am always looking for ways to improve my formatting skills. While a great deal of formatting skill is art (and personal taste), there are several ground rules to follow as well. Applying ideas like consistency, alignment, simplicity and vibrancy goes a long way.
What formatting tips & ideas you follow? Please share them with us using comments.
Learn how to make better spreadsheets
- 10 tips to make spreadsheets that your boss will love
- 5 conditional formatting basics to master
- 12 Rules for making better spreadsheets
- More tips on formatting, conditional formatting, custom cell formatting & chart formatting
Join Excel School & Make awesome Excel sheets
In my Excel School program, we focus not just on teaching Excel, but also teaching you how to make awesome Excel workbooks. You can see how I format my data, charts, dashboards & reports and learn hundreds of tips on formatting.
Even the lesson workbooks are beautifully formatted & packed with fresh ideas for you to try.
Consider joining our Excel School program, because you want to be awesome in Excel.





















8 Responses to “Introducing PHD Sparkline Maker – Dead Simple way to Create Excel Sparklines”
This looks like it could be very useful for a project I'm putting together right now, thank you so much. Quick & silly question, how do I copy & paste the sparkline as a picture?
Question answered. For anyone else:
Select chart>Hold Shift key & select Edit/Copy Picture>Paste
[...] more information about PHD Sparkline Maker, please read this article and to learn more about Sparklines, read this article from Microsoft Excel 2010 blog. Also there [...]
Am I right in thinking that the y-axis is set automatically by excel?
That makes it possible to get the column chart not to start at zero.
Andy - yes, it is currently set to 'auto', which defaults to a zero base for positive values, but you can change that by left-clicking the chart, then choosing (in Excel 2007):
"Chart Tools/Layout/Axes/Primary Vertical Axis/More Primary Vertical Axis Options"
PUBLIC SERVICE ANNOUNCEMENT: When manually editing a chart's minimum/maximum axis values, PLEASE be sure there's a valid reason and that doing so won't skew the message shown by the data (e.g. by exaggerating differences). If in doubt, go back and read Tufte. (W.W.T.D.?)
[...] gridlines, axis, legend, titles, labels etc.) and resize it so that it fits nicely in a cell [example]. This is the easiest and cleanest way to get sparklines in earlier versions of excel. However this [...]
thanks for the work creating the template!!!!
looks good