One of the most dreaded courses during my under-graduation is Probability, Statistics & Queuing Theory. We called it PSQT. I struggled to understand the significance and concept of this course as I could barely concentrate in the class. We had a professor, who is probably a genius, but the moment he started the class, I would magically fall in to one of my after-noon naps. When I woke up, we are either in the middle of an elaborate t-test or going thru intricacies of a Markovian queue.
This was all 11 years ago. Later in life, I have embraced the world of probability & statistics. I still fear queues. May be I will get there one day. 😉
A good understanding of statistics & probability theory is necessary if you want to model complex real-life problems using Excel or similar tools. Naturally, Excel has several functions, features & supported add-ins to help you in this area.
Today, I want to share some of this with you. This article is broken down in to 3 parts.
- Learning Statistics & Probability using Excel
- Downloadable Excel Workbooks to understand
- Full blown models & simulations in Excel
#1 – Learning Statistics & Probability Concepts using Excel
Using Excel RAND functions
Excel has several powerful functions (formulas) to generate random numbers, random data. You can combine these functions to generate data that has certain parameters – like a give mean, standard deviation or follows a certain type of distribution.
Go thru Using Excel’s Random Functions for a detailed overview these techniques.
Simulating Dice Throws in Excel
One of the fundamental ways to learn about Probability is to look at dice throws. A dice has 6 faces and on each throw, any of the 6 faces turning up is equally likely. So, we say, each face has 1/6th probability of showing up. If you want to simulate this in Excel, you can use the formula RANDBETWEEN like this, =RANDBETWEEN(1,6). On each run, this formula would throw up a random number between 1 & 6 (including both).
For more, Simulating Dice Throws in Excel
Shuffling a List of Values in Excel
Understanding permutations and combinations is essential when it comes to modeling many real-world problems. Using Excel’s RAND, VLOOKUP and SMALL formulas we can generate a random permutation of a given list of values (in other words – we can shuffle the list).
To learn this read, Shuffling a list of values in Excel
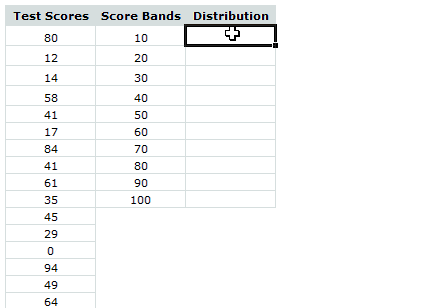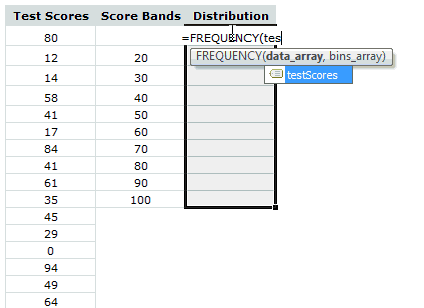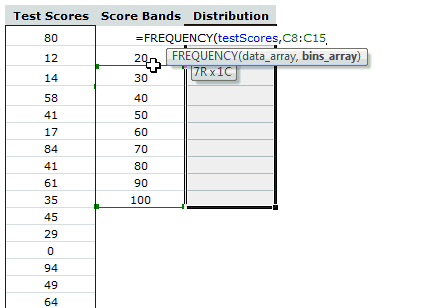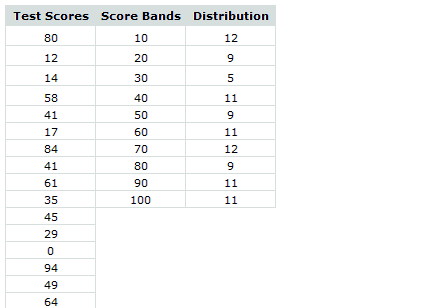
Generate Frequency Distribution from Data
Often, when you are analyzing data, you need to understand how the data is distributed. Again, Excel has just the right function for this sort of thing. FREQUENCY(). In this simple tutorial, learn how to use Excel’s FREQUENCY formula to generate frequency distribution of given data.
Read Frequency Distributions in Excel
Trend Analysis & Forecasting using Excel
One of the most common applications of statistics is trend analysis & forecasting. Again, Excel shines with a lot of powerful formulas, built-in features and charting tools to help you understand the data & predict future based on that.
Since this is a big topic, we have covered it in 3 parts –
Part 1- Introduction to Trend Analysis & Forecasting: In this, we will learn what is trend analysis & forecasting. We will see manual forecasting technique in Excel. We will use Excel charts to depict our analysis and results.
Part 2 – Trend Analysis & Forecasting using Excel Functions
In this second part, we learn about Excel’s functions like LINEST, TREND, FORECAST, SLOPE, INTERCEPT, LOGEST and GROWTH. These powerful formulas can process lots of data and extract the trend information dynamically.
Part 3 – Trend Analysis & Forecasting using Charts & Macros
In the final part, we talk about how to use Excel chart’s trend analysis & forecasting features to estimate the trend & predict future values based on the data.
We also learn how to use Macros (VBA) to augment Excel chart’s trend-lines with useful information.
Visualizing Distribution of data with Box Plots
Box plots are an excellent way to understand the distribution of data. Unfortunately, there is no direct option to make a box plot from given data in Excel. That is where, this tutorial comes handy.
Learn how to create box plots in Excel.
#2 Downloadable Excel Workbooks
Learn Basic Statistics & Gaussian Distribution using this Excel Workbook
Glen, one of our long time readers shared this file with me. It lets you perform statistical analysis, quality control analysis, visualize Gaussian distribution based on the data you enter.
Click here to download the workbook.

Thanks Glen.
More Downloadable Workbooks
Almost all of the links in this page will take you to detailed articles on Chandoo.org, where you can also find downloadable workbook with examples. So just click thru and learn. 🙂
#3 Full blown models & simulations in Excel
A full blown model lets you learn various statistical concepts, Excel features and how to bring them all together to mimic a real-life situation.
Simulating Deal or No Deal game in Excel
In this simulation of Deal or No Deal, a popular television game, we use basic probability, permutations and Excel formulas features. You will learn how to assign random values to the suit-cases, how to use circular references, how to calculate the banker’s offer.
Simulation of Deal or No Deal game in Excel
Generating Housie / Bingo Tickets in Excel
Housie (Bingo) is a popular recreational game where the tickets contain 15 numbers between 1 to 90, arranged in 10 columns (3×10 grid). First column has numbers between 1 to 9, second column has 10 to 19 so on..
Generating a bingo ticket in Excel is a nice exercise in statistics, permutations and Excel formulas.
Learn from Bingo / Housie Tickets in Excel
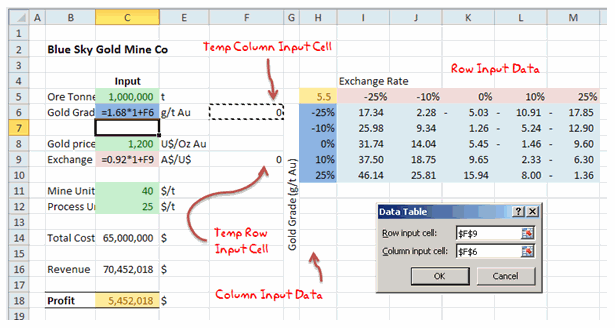
Data Tables & Monte Carlo Simulations in Excel
Excel has powerful features to let us do complex simulations of real world situations. One such feature is called as data table.
The Data Table allows a set of what if questions to be posed and answered simply, and is useful in sensitivity analysis, variance analysis and even Monte Carlo (Stochastic) analysis of real life model within Excel.
The case of Blue Sky Mining Company
To help you learn about data tables, Monte Carlo simulations, we have put together a fictional mining company – Blue Sky co. and analyzed its performance under various assumptions & simulations.
To learn about this, visit Data Tables & Monte-Carlo Simulations page.
Modeling & Scheduling a FIFO (First In First Out) Queue in Excel
FIFO queues are very common in life. You can see them at Airports, coffee shops, Apple stores; Except at Airports it is FIFOUYC (FIFO Unless You are Crew).
In this article, we model & schedule a FIFO queue using Excel.
More Full Blown Models & Simulations in Excel
For more examples, check out these links.
- One more example of Data Table & Linest
- Simulating 3D dancing pendulums in Excel
- Simulating Monopoly Board Game in Excel
Do you use Statistical Concepts for your work?
As a small business owner, a good portion of my work involves statistical analysis, forecasting and simulation. I run estimates for our website traffic, revenues. I run statistical tests (split tests etc.) to optimize our sales pages, website. I estimate when my kids wake up from their nap (based on past experience) and plan my work accordingly. Thankfully, for the last part, I do not use Excel 😀
What about you? Do you use statistical concepts for your work? What are the things you use and how does Excel help you in that? What are your favorite formulas, features and tips? Please share using comments.
Special thanks to Hui & Glen
Many thanks to Hui, our resident Excel ninja for writing many of the articles on statistics, simulation, forecasting & trend analysis.
Special thanks to Glen for sharing the analyze-this file with us.
Say thanks to them if you enjoyed this.

























8 Responses to “Pivot Tables from large data-sets – 5 examples”
Do you have links to any sites that can provide free, large, test data sets. Both large in diversity and large in total number of rows.
Good question Ron. I suggest checking out kaggle.com, data.world or create your own with randbetween(). You can also get a complex business data-set from Microsoft Power BI website. It is contoso retail data.
Hi Chandoo,
I work with large data sets all the time (80-200MB files with 100Ks of rows and 20-40 columns) and I've taken a few steps to reduce the size (20-60MB) so they can better shared and work more quickly. These steps include: creating custom calculations in the pivot instead of having additional data columns, deleting the data tab and saving as an xlsb. I've even tried indexmatch instead of vlookup--although I'm not sure that saved much. Are there any other tricks to further reduce the file size? thanks, Steve
Hi Steve,
Good tips on how to reduce the file size and / or process time. Another thing I would definitely try is to use Data Model to load the data rather than keep it in the file. You would be,
1. connect to source data file thru Power Query
2. filter away any columns / rows that are not needed
3. load the data to model
4. make pivots from it
This would reduce the file size while providing all the answers you need.
Give it a try. See this video for some help - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5u7bpysO3FQ
Normally when Excel processes data it utilizes all four cores on a processor. Is it true that Excel reduces to only using two cores When calculating tables? Same issue if there were two cores present, it would reduce to one in a table?
I ask because, I have personally noticed when i use tables the data is much slower than if I would have filtered it. I like tables for obvious reasons when working with datasets. Is this true.
John:
I don't know if it is true that Excel Table processing only uses 2 threads/cores, but it is entirely possible. The program has to be enabled to handle multiple parallel threads. Excel Lists/Tables were added long ago, at a time when 2 processes was a reasonable upper limit. And, it could be that there simply is no way to program table processing to use more than 2 threads at a time...
When I've got a large data set, I will set my Excel priority to High thru Task Manager to allow it to use more available processing. Never use RealTime priority or you're completely locked up until Excel finishes.
That is a good tip Jen...