Today we will learn a new and exciting excel formula – the all powerful SUMPRODUCT.
At the outset SUMPRODUCT formula may not seem like all that useful. But once you understand how excel works with lists (or arrays) of data, the SUMPRODUCT’s relevance becomes crystal clear.
SUMPRODUCT formula – syntax and usage
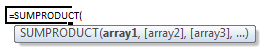 The sum-product formula syntax is very simple. It takes 1 or more arrays of numbers and gets the sum of products of corresponding numbers.
The sum-product formula syntax is very simple. It takes 1 or more arrays of numbers and gets the sum of products of corresponding numbers.
The syntax is =SUMPRODUCT (list 1, list 2 ...)
 So, for ex: if you have data like {2,3,4} in one list and {5,10,20} in another list, and if you apply SUMPRODUCT, you will get 120 (because 2*5 + 3*10 + 4*20 is 120).
So, for ex: if you have data like {2,3,4} in one list and {5,10,20} in another list, and if you apply SUMPRODUCT, you will get 120 (because 2*5 + 3*10 + 4*20 is 120).
At this point it might seem like an almost useless function. But all that will change in the next 2 minutes, keep reading.
SUMPRODUCT and Arrays
Lets say you have a list of sales data with columns Name, Region, Product and Sales. Now, you want to know how many units the sales person named “Luke” sold. This is simple, you will write a SUMIF formula [examples] and use the Name column as “criteria range” and Sales column as “sum range”.
But, wait a second, you want to find how many units sales person “Luke” sold in the region “west”.
Hmm…. we have 2 options,
- Use an array formula
- Use a pivot table [what is a pivot table?]
Actually, there is a hidden third option, use SUMPRODUCT.
That is right, my friend, we can use SUMPRODUCT to do just this (and much more).
Using SUMPRODUCT as an array formula
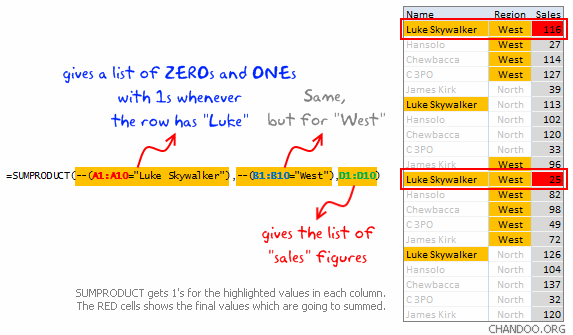
Assuming, the data is in range A1:D10, with Name in column A, Region in B, Product in C and Sales in D, the SUMPRODUCT formula is,
=SUMPRODUCT(--(A1:A10="Luke Skywalker"),--(B1:B10="West"),D1:D10)
Okay, lets take a minute and try to understand WTF (what the formula) is doing.
- The portion
--(A1:A10="Luke Skywalker")is looking for Luke Skywalker across planetary systems in all universes 😉 It is going to give us a bunch of ONEs and ZEROs, one if the cell has Luke, Zero if the cell has something else. - The portion
--(B1:B10="West")is doing the same, but gets 1s when the value is “West”. - The portion
D1:D10is just returning all the sales figures. - When you put everything together and multiply, it just works. Why? That is your home work to figure out.
Share your SUMPRODUCT formula Tips & Tricks
SUMPRODUCT formula can do much more once you understand how it works. This post is meant to open the door for you. Go ahead and explore the possibilities, then come back and share your tips with us.
Recommended Reading
I suggest reading the excel array formula examples, sumif with multiple conditions and other excel formula tutorials.
This post is part of our spreadcheats series


















One Response to “Excel Tips Submitted by You [Part 4]”
ctl+d
copy the up cell