This is a guest post by Daniel Ferry of Excelhero.com.
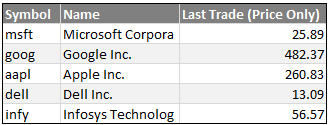 Have you ever wanted to fetch live stock quotes from excel? In this post we will learn about how to get stock quotes for specified symbols using macros.
Have you ever wanted to fetch live stock quotes from excel? In this post we will learn about how to get stock quotes for specified symbols using macros.
One method that has worked well for my clients can be implemented with just a few lines of VBA code. I call it the ActiveRange.
An ActiveRange is an area on a worksheet that you define by simply entering the range address in a configuration sheet. Once enabled, that range becomes live in the sense that if you add or change a stock symbol in the first column of the range, the range will automatically (and almost instantly) update. You can specify any of 84 information attributes to include as columns in the ActiveRange. This includes things such as Last Trade Price, EBITDA, Ask, Bid, P/E Ratio, etc. Whenever you add or change one of these attributes in the first row of the ActiveRange, the range will automatically update as well.
Sound interesting, useful?
In this post, you can learn how to use excel macros to fetch live stock quotes from Yahoo! Finance website. It is also going to be a crash course in VBA for the express purpose of learning how the ActiveRange method works so that you can use it yourself.
Download Excel Stock Quotes Macro:
Click here to download the excel stock quotes macro workbook. It will be much easier to follow this tutorial if you refer to the workbook.
Background – Understanding The Stock Quotes Problem:
The stock information for the ActiveRange will come from Yahoo Finance. A number of years ago, Yahoo created a useful interface to their stock data that allows anyone at anytime to enter a URL into a web browser and receive a CSV file containing current data on the stocks specified in the URL. That’s neat and simple.
But it gets a little more complicated when you get down to specifying which attributes you want to retrieve [information here]. Remember there are 84 discreet attributes available. Under the Yahoo system, each attribute has a short string Tag Code. All we need to do is to concatenate the string codes for each attribute we want and add the resulting string to the URL. We then need to figure out what to do with the CSV file that comes back.
Our VBA will take care of that and manage the ActiveRange. Excel includes the QueryTable as one of its core objects, and it is fully addressable from VBA. We will utilize it to retrieve the data we want and to write those data to the ActiveRange.
Before we start the coding we need to include two support sheets for the ActiveRange. The first is called “YF_Attribs”, and as the name implies is a list of the 84 attributes available on Yahoo Finance along with their Yahoo Finance Tag Codes. The second sheet is called, “arConfig_xxxx” where xxxx is the name of our sheet where the ActiveRange will reside. It contains some configurable information about the ActiveRange which our VBA will use.
All of the VBA code for this project will reside inside of the worksheet module for the sheet where we want our ActiveRange to be. For this tutorial, I called the sheet, “DEMO”.
Writing the Macros to Fetch Stock Quotes:

Press ALT-F11 on your keyboard, which will open the VBE. Double click on the DEMO sheet in the left pane. We will enter out code on the right. To begin with, enter these lines:
Private rnAR_Dest As Range
Private rnAR_Table As Range
Private stAR_ConfigSheetName As String
Always start a module with Option Explicit. It forces you to define your variable types, and will save you untold grief at debugging time. In VBA each variable can be one of a number of variable types, such as a Long or a String or a Double or a Range, etc. For right now, don’t worry too much about this – just follow along.
Sidebar on Variable Naming Conventions
Variable names must begin with a letter. Everyone and their brother seems to have a different method for naming variables. I like to prefix mine with context. The first couple of letters are in lower case and represent the type of the variable. This allows me to look at the variable anywhere it’s used and immediately know its type. In this project I’ve also prefaced the variables with “AR_” so that I know the variable is related to the ActiveRange implementation. In larger projects this would be useful. After the underscore, I include a description of what the variable is used for. That’s my method.
In the above code we have defined three variables and their types. Since these are defined at the top of a worksheet module, they will be available to each procedure that we define in this module. This is known as scope. In VBA, variables can have scope restricted to a procedure, to a module (as we have done above), or they can be global in scope and hence available to the entire program, regardless of module. Again we are putting all of the code for this project in the code module of the DEMO worksheet. Every worksheet has a code module. Code modules can also be added to a workbook that are not associated with any worksheet. UserForms can be added and they have code modules as well. Finally, a special type of code module, called a class module, can also be added. Any global variables would be available to procedures in all of these. However, it is good practice to always limit the scope of your variables to the level where you need them.
In that vein, notice that the three variables above are defined with the word Private. This specifically restricts their scope to this module.
Every worksheet module has the built-in capability of firing off a bit of code in response to a change in any of the sheet’s cell values. This is called the Worksheet_Change event. If we select Worksheet from the combo box at the top and Change in the other combo box, the VBE will kindly define for us a new procedure in this module. It will look like this:
![]()
End Sub
Notice that by default this procedure is defined as Private. This is good and as a result the procedure will not show up as a macro. Notice the word Target near the end of the first line. This represents the range that has been changed. Place code between these two lines so that the entire procedure now looks like this:
The Heart of our Excel Stock Quotes Code – Worksheet_Change()
ActivateRange
If Worksheets(stAR_ConfigSheetName).[ar_enabled] Then
If Intersect(Target, rnAR_Dest) Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
If Target.Column <> rnAR_Dest.Column And Target.Row <> rnAR_Dest.Row Then
PostProcessActiveRange
Exit Sub
End If
ActiveRangeResponse
End If
End Sub
That may look like a handful but it’s really rather simple. Let’s step through it. The first line is ActivateRange. This is the name of another sub-procedure that will be defined in a moment. This line just directs the program to run that sub, which provides values to the three variables we defined at the top. Again, since those variables were defined at the top of the module, their values will be available to all procedures in the module. The ActivateRange procedure gives them values.
Next we see this odd looking fellow:
If Intersect(Target, rnAR_Dest) Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
All this does is check to see if the Target (the cell that was changed on the worksheet) is part of our ActiveRange. If it is the procedure continues. If it’s not, the procedure is exited.
The next line checks to see if the cell that was changed is in the first column or first row of the ActiveRange. If it is, the post processing is skipped. If the change is any other part of the ActiveRange, another sub-procedure (defined below) is run to do some post processing of the retrieved data, and then exits this procedure.
If the cell that changed was in the first column or the first row, the program runs another sub-procedure, called ActiveRangeResponse, which is also defined below. ActiveRangeResponse builds the URL for YF, deletes any previous QueryTables related to the ActiveRange, and creates a new QueryTable as specified in our configuration sheet.
That’s it. The heart of the whole program resides here in the Worksheet_Change event procedure. It relies on a number of other subprocedures, but this is the whole program. When a change is made in the ActiveRange’s first column (stock symbols) or its first row (stock attributes), ActiveRangeResponse runs and our ActiveRange is updated.
Understanding other sub-procedures that help us get the stock quotes:
So let’s look at those supporting subprocedures. The first is ActivateRange:
stAR_ConfigSheetName = “arConfig_” & Me.Name
Set rnAR_Dest = Me.Range(Worksheets(stAR_ConfigSheetName).[ar_range].Value)
Set rnAR_Table = rnAR_Dest.Resize(1, 1).Offset(1, 1)
Worksheets(stAR_ConfigSheetName).[ar_YFAttributes] = GetCurrentYahooFinancialAttributeTags
End Sub
Again, all this does is give values to our three module level variables. In addition it builds the concatenated string of YF Tag Codes required for the URL. It does this by calling a function that I’ve defined at the very bottom of the module, called GetCurrentYahooFinancialAttributeTags.
The next subprocedure is ActiveRangeResponse:
Dim vArr As Variant
Dim stCnx As String
Const YAHOO_FINANCE_URL = “http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes.csv?s=[SYMBOLS]&f=[ATTRIBUTES]”
vArr = Application.Transpose(rnAR_Dest.Resize(rnAR_Dest.Rows.Count – 1, 1).Offset(1))
stCnx = Replace(YAHOO_FINANCE_URL, “[SYMBOLS]”, Replace(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Join(vArr)), ” “, “+”))
stCnx = Replace(stCnx, “[ATTRIBUTES]”, Worksheets(stAR_ConfigSheetName).[ar_YFAttributes])
AddQueryTable rnAR_Table.Resize(UBound(vArr)), “URL;” & stCnx
End Sub
Notice that here we have variables defined at the top of this procedure and consequently their scope is limited to this procedure only. This means that we could have the same variable names defined in other procedures but those variables would not be related to these and would have completely different values.
Next notice that we have defined a constant. This is good practice, as it forces us to specify what the constant value is by naming the constant. I could have just used the value where I later use the constant, but then the question arises as to what is this value and where did it come from. Here I have named the value, YAHOO_FINANCE_URL, removing all doubt as to its purpose.
The next line is this:
vArr = Application.Transpose(rnAR_Dest.Resize(rnAR_Dest.Rows.Count - 1, 1).Offset(1))
and it deserves some explanation. Let me back up by saying that whenever we write or read multiple cells from a worksheet we should always try to do it in one go, rather than one cell at a time. The more cells involved the more important this is. Otherwise we pay a massive penalty in processing time. One of the best optimization techniques available is to replace code that loops through cell reads/writes and replace it with code that reads/writes all the cells at once. It can literally be hundreds to thousands of times faster.
Here we are interested in getting the list of all of the stock symbols in the first column of the ActiveRange. So how do we get them in one shot? We use something called a variant array. Notice that we defined vArr at the top of this procedure. A variant array is a special kind of variable that holds a list of values and it DOES NOT CARE what variable types those values are. This is important when retrieving data from a sheet because the data could be numbers, text, Boolean (True or False), etc. Variants are powerful, but they are much slower than other variable types, such as a Long for numeric data for example. However, in the case of retrieving or writing large chunks of data from/to a sheet the slight penalty of the variant is dwarfed by the massive increase in the speed of data transfer.
It’s very simple to retrieve range data (regardless of the size) into a variant array. All you do is:
v = range
where v is defined as a variant and range is any VBA reference to a worksheet range. And magically all of the values in that range are now in v. Note that v is not connected to the range. A change in any of v’s values does not propogate back to the range, and likewise a change to the range does not make it’s way to v all by itself. v will ALWAYS be a two-demensional array. The first dimension is the index of the rows, the second dimension is the index of the columns. So v(1,1) will refer to the value that came from the top left cell in the range. v(6,9) will hold the value that came from the cell in the range at row 6 and column 9.
For most circumstances this two-dimensional format is fine. But we are only retrieving one column of stock symbols. The procedure will still give us a two-dimensional array, with the column dimension being only 1 element wide. This is a shame because VBA has a wonderful function called Join that allows you in one step (no loop) to concatenate every element of an array into a string. You can even specify a custom string to delimit (go in-between) each element in the output string. The problem is that Join only works on single dimensioned arrays 🙁
But there’s always a way, right? We can use the Application.Transpose method on the 2-D array and presto we get a 1-D array. The rest of the line just specifies what range (the stock symbols) to grab.
The next two lines are:
stCnx = Replace(YAHOO_FINANCE_URL, "[SYMBOLS]", Replace(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Join(vArr)), " ", "+"))
stCnx = Replace(stCnx, "[ATTRIBUTES]", Worksheets(stAR_ConfigSheetName).[ar_YFAttributes])
Again a handful, but all we are doing here is replacing the monikers, [SYMBOLS] and [ATTRIBUTES] in the YAHOO_FINANCE_URL constant with the list of stock symbols (delimited by a plus sign) and the string of attributes.
In the final line of the procedure:
AddQueryTable rnAR_Table.Resize(UBound(vArr)), "URL;" & stCnx
we are running another subprocedure called, AddQueryTable and we are telling it where to place the new QueryTable and providing the connection string for the QueryTable, which in this case is the YF URL that we just built.
Nothing unusual happens in the AddQueryTable sub. It just deletes any existing AR related QueryTables and adds the new one according to the options in the configuration sheet.
The PostProcessActiveRange sub is interesting:
If rnAR_Dest.Columns.Count > 2 Then
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
rnAR_Table.Resize(rnAR_Dest.Rows.Count).TextToColumns Destination:=rnAR_Table, DataType:=xlDelimited, Comma:=True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Worksheets(stAR_ConfigSheetName).[ar_LocalTimeLastUpdate] = Now
End If
End Sub
Processing Yahoo Finance Output using Query Table & Text-Import Utility:
As mentioned before the data from YF comes back as a CSV file. The QueryTable dumps this into one column. If you were only retrieving one attribute for each stock this would be fine as is. However, two or more attributes is going to result in unwanted commas and multiple attribute values squished into the first column of the QueryTable output. Unfortunately this is poor design by Microsoft, especially when you consider that the QueryTable does not behave like this when it is retrieving SQL data or opening a Text file from disk. You can actually specify this operation to be a text file and it will properly spread the output over all of the columns. To do so, you specify the disk location as being the URL of the YF CSV file, but as Murphy would have it, it’s unbelievably slow and pops up a status dialog as it slowly retrieving the CSV. Using the URL instruction instead of the TEXT instruction at the beginning of the connection string is incredibly fast in comparison, but dumps all of the data into the first column.
So what to do? We’ll just employ Excel’s built-in TextToColumns capability and bam, our data is where we want it.
Our finalized stock quotes fetcher worksheet should look like this:

Download Excel Stock Quotes Macro:
Click here to download the excel stock quotes macro workbook. It will be much easier to follow this tutorial if you refer to the workbook.
Final Thoughts on Excel Stock Quotes
The ActiveRange technique is quite versatile. It can be implemented with other data sources such as SQL, or even lookups to other Excel files, or websites.
In this example it provides a nice way to easily track whatever stocks you may have interest in and up to 84 different attributes of those stocks. You can enable and disable the activeness of the ActiveRange on the fly. You can set the AR to AutoRefresh the data at periods that you set or to not refresh at all.
This is a basic implementation. For example, changing the AutoRefresh setting will have no effect until a new QueryTable is built. That won’t happen until you also add or change a stock symbol or add or change an attribute. An easy enhancement would be to add a little code to the arConfig_DEMO code module to respond to changes to the ar_AutoRefresh named range cell.
Another enhancement would be to eliminate the slight flicker of the update by moving the QueryTable destination to the arConfig_DEMO and then doing the TextToColumns with the destination set to the DEMO sheet. In an effort to simplify this tutorial I have left these easy enhancements as an exercise for you to implement.
Have a question or doubt? Please Ask
Do you have any questions or doubts on the above technique? Have you used ActiveRange or similar implementations earlier? What is your experience? Please share your thoughts / questions using comments.
I read Chandoo.org regularly and will be monitoring the post for questions. But you can also reach me at my blog:
Further References & Help on Excel Stock Quotes [Added by Chandoo]
- Fetching Stock Quotes using Research Pane
- Stock Portfolio Tracker using Google Docs
- QueryTable Object Model & Properties
- Using QueryTable to Generate Dynamic Reports
- Yahoo Finance API Documentation & Example
Excel Hero is dedicated to expanding your notion of what is possible in MS Excel and to inspiring you to become an Excel Hero at your workplace. It has many articles and sample workbooks on advanced Excel development and advanced Excel charting.


















28 Responses to “Team To Do Lists – Project Tracking Tools using Excel [Part 2 of 6]”
[...] & tracking a project plan using Gantt Charts Team To Do Lists - Project Tracking Tools Part 3: Preparing a project time line [upcoming] Part 4: Time sheets and Resource management [...]
the templates are great (I bought the combo).
What I'm missing is a way to have the project gantt chart and reporting with the data per resource, in such a way that I can also show the occupation per resource on an extended gantt chart.
So with hours entered per person per project or sub-activity, to show a gantt chart of how many hours/days a person spent on which project (or plans to spend).
[...] from: Team To Do Lists - Project Tracking Tools using Excel [Part 2 of 6] 25 Jun 09 | [...]
Hi Chandoo,
Funny I have a post on the value of MS project lined up which I will post when the current monster project I'm working on finishes and I get some free time!
I'm not sure this would help with any of the projects I've worked on, closing down a to do list seems like more effort than it's worth, but it might be useful for some things. I guessing it doesn't, but does the time stamp not update when you recalculate the work book?
keep up the good work!
Ross
@Ross.. Thanks for sharing your ideas... I think to do lists are a great way to keep up with project activities and ensure accountability from individual team members, when they are implemented right.
"I guessing it doesn’t, but does the time stamp not update when you recalculate the work book?"
Your guess is right. When you change the calculation mode to "iterative", excel takes care of the nittygritties and retains older values in circular references in formulas.
[...] Project Management in Excel [New Series] - Gantt Charts | To Do Lists [...]
[...] & tracking a project plan using Gantt Charts Team To Do Lists - Project Tracking Tools Project Status Reporting - Create a Timeline to display milestones Part 4: Time sheets and Resource [...]
Hi Chandoo,
The template give me lot of convenience to monitor the thing to do. It simple. Thank You
[...] & tracking a project plan using Gantt Charts Team To Do Lists - Project Tracking Tools Project Status Reporting - Create a Timeline to display milestones Part 4: Time sheets and Resource [...]
[...] make sure you have read the first 4 parts of the series - Making gantt charts [project planning], team todo lists [project tracking], project time lines chart [reporting] and Timesheets and Resource Management using Excel. Also [...]
Chandoo,
I really do not see any befit to this function in Excel unless it was somehow tied into some other chart. That is say a scheduled activities % complete is based on the to-do list.
The only way this chart would be useful is if no one was assigned none dependent task that could be done by anyone. The cases were both of these conditions are true are so few and far between it really makes this chart worthless.
@Brian... Once you have a todo list up and running, it is easy to get metrics out of it. I didnt propose it as it might look a bit too micro-management-ish.
I am able to understand what you meant by "The only way this chart would be useful is if no one was assigned none dependent task that could be done by anyone. The cases were both of these conditions are true are so few and far between it really makes this chart worthless."
Can you explain?
"Chandoo"
What I mean is this. Lets say you have 10 task which are part of one activity/WBS that is in your schedule. One there are very few cases were many people would be assigned to complete this one scheduled activity with no direction being given who should what of the 10 task. It is poor management, and the task 90% of the time would not get done in a timely manner if say 4 people were responsible. Secondly, you are assuming all 10 task are independent of each other. You might need to do task 1 thru 3 before you can do task 4, and to do task 7 you might need to do 4 and 6. Thirdly, the time it would take to compile and then fill out the to-do-list even in limited applications is really not worth it.
I just see almost no applications why a team would need to inform others separate from the schedule that they have completed a task on a to-do list unless anyone of the 4 people could of completed that task.
My point is, there might be a few very limited applications for this type of list but this list would be worthless as a Project Management tool in every other case.
However, change this from a to-do-list to a document change log and it is perfect. Instead of to-do it is the documents name or summary of what changed in the document. The person is who edited the document, and the time stamp is when they checked it in. But I do not know why you would use excel when there is free software you can use commercially that is 10 times better that does document management.
I think using excel to do Project Management over a real Project Management application is a bad idea. Unless you are running a very small, simple project, the time and effort is a lot more to use excel compared to the cost of the Project Management software.
This comes back to my point, I love your site, however, just because you can do something in excel does not mean you should do it. To often the time it takes to use excel is wasted 10 times over from the cost of doing it in an application designed to for the specific application.
@Brian: The todo list mentioned here is meant to keep track of all the tasks for which detailed planning is not necessary but some sort of tracking is needed. These are not be confused with project activities (a la gantt chart).
I like your suggestion about using this as a document tracker. Pretty cool use.
Coming to your point about excel as a real project management tool, well, I have my views, but in a serious project environment, it would surely payoff to have a dedicated project management application.
[...] & tracking a project plan using Gantt Charts Team To Do Lists – Project Tracking Tools Project Status Reporting – Create a Timeline to display milestones Time sheets and Resource [...]
Chandoo,
Wonder how the timestamp column will maintain its previous data. Both Today() and Now() functions will update as and when the next timestamp happens.
[...] Preparing & tracking a project plan using Gantt Charts Part2: Team To Do Lists – Project Tracking Tools Part3: Project Status Reporting – Create a Timeline to display milestones Part4: Time sheets and [...]
I've combined this with the issue tracker since I like the automatic date stamp, but one thing I'm noticing is that I can't replicate the chart that goes along with the issue tracker because the cells that are referenced have the formula that inserts the time stamp instead of a the actual date value. All the dates of the last 30 days display 0 when they should have a value.
Is there a way around this?
I have edited the chart so that my team members can update the percentage completion of the assigned tasks. When the cell is updated, i would like the time stamp to update. How would I manipulate the formula to update whenever the drop-down list is changed?
[...] … ??? To Do List [...]
Excel is great however sometimes you need to get a better idea of what tasks each person on your team is working on at any given time. We've developed a web app that can do just that! Each person has a list of tasks, listed in the order they have to complete them.
HII,
I want to expand the database through excel where i am working on 11 cities as of now and i want to expand it upto 50 cities and hence forth the data related to it will also expand so i want to make it precise where i can get updates also that this work is required to be done at that particular day or date
Thanks for making all of this information available for free. I am currently using excel to track everything for the first time. I later plan to output our information here with a more visual presentation. Wish me luck!
Can some one point me out to some additional direction on the "Who Finished it?" column? Something more 'basic' for a newbie excel guy? lol I got everything else working on this tutorial but that column. I can't seem to recreate it and I know a lot of it is due to lack of knowledge with VB code. I'd like to recreate this column very much 🙁
Dear Chandoo,
Thanks for the team to do list, kindly let me know how to set the column who " finished it " from another work sheet
Hi Chandoo,
Unable to download it - can you please check the link and confirm.
Great inhisgt! That's the answer we've been looking for.
Hi Team,
I know u all are the best programmers in the world!!! that's I am here to rectify my issues. here is my question please ans me as soon as possible before 8-3-2017 its really urgent.
I have a project named the production tracker.
1) I require the user form which shows the names of the Associates which are linked to the different tracks. when the user is selected the particular track related details and dropdowns should appear.
2) I need to track the associate needs how much of the time to complete the particular task. with start stop and pause and resume timer.
3) It should display the daily count of the production and save the data to the another Excel file.
this production tracker should save all the data no matter how many people logs in into it.
Please help me for this it will be very appreciated.
you can directly email me on my mail ID: tusharkch694@gmail.com