My friend Paresh writes excellent commentary on charts on his blog Visual Quest. Last week he gave a home work, asking his readers to recreate the small multiples chart shown below.
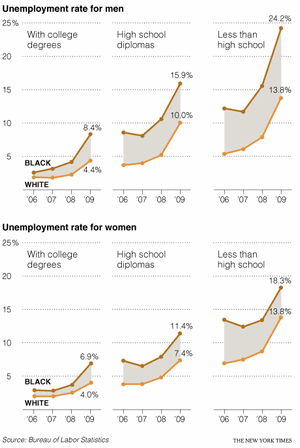
I found this quite interesting. Small multiples, also called as panel charts, are a powerful way to depict multidimensional data and bring out insights. They are easy to read too.
So, today, let us learn how to create such charts using Excel.
Step 1: Arrange your data
Almost any chart or visualization worth its salt must begin with proper arrangement of data. Since I could not get the data for the unemployment chart, I made up a few numbers for a fictional Confectionery Company. The data is shown below.
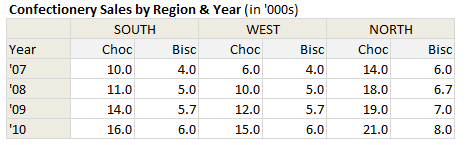
So, we have the data for years 2007 thru 2010, for the regions – South, West & North and for the product lines – Chocolates & Biscuits
Step 2: Select Products for one region & make an area chart
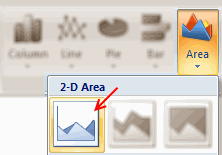
This is simple. Just select data for chocolates & biscuits for one region and make an area chart. You should have something like this:
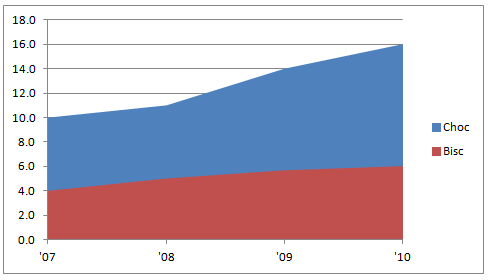
Step 3: Resize the area chart & format it
Now, we need to make this area chart closer to what we want.
- Select the bottom area series and fill it with white color.
- Now resize the chart so that we can fit 3 of them in the area you got.

Step 4: Add same data to the chart
Now, select the same region data, press CTRL+C to copy it. Select the chart and paste it by pressing CTRL+V. See below demo to understand how to do this.

We are doing this because we want to have lines with markers on our chart. But the area chart lines cannot show markers. So we are going to add the same data one more time, but this time format it to be shown as a line.

Step 5: Select the new series and format them as line charts
Select each of the new area series and format as line chart with markers.
You should have something like this at the end.

Step 6: Format the chart
This is where you unleash the creativity. In order to match the look of NYTimes chart, here is what you can do.
- Set the fill color between lines to something dull.
- Format 2 lines in distinct colors.
- Format gridlines & axis lines to something dull.
- Set axis maximum to 25 (as all charts in small-multiples should have same axis settings)
- Set axis major unit to 5.

Step 7: Repeat this for other regions
Now, just copy and paste this chart a couple of times. Just adjust the data source so that we have new charts using this technique.

Note: Learn how you can add descriptive labels to charts.
That is all. You just made a small multiples chart that looks awesome. Congratulations.
Download Small Multiples Example Workbook
Click here to download the example workbook and play with it. You can see the steps for making one of the charts in the workbook as well.
Do you use Small Multiples or Panel Charts?
I really love to use small multiples or panel charts whenever I am analyzing data or presenting results of the same. They offer excellent value per pixel. That said, they take some time to construct. Also, you must tweak axis settings and plot area to get the perfect result. That is why I prefer the in-cell variation of these charts. They are quick to setup and easy to wow (for more on these techniques, see below).
What about you? Do you use Small Multiples or Panel charts? How do you find them? Please share using comments.
Interested to learn more? Read these
As you can guess, small multiples is one of my favorite ways to explore and present data. So we have written quite a few articles explaining this technique. Read these to learn more.





















9 Responses to “Show forecast values in a different color with this simple trick [charting]”
While this works in a pinch, it clearly "lightens" the colors of the entire chart. Depending on where you use this, it will be blatantly obvious that you don't know what you are doing and present a poor looking graph.
Why not separate the data into different segments when charting and have as many colors as you have data points? You might have to create a new legend and/or repeat the chart in "invisible ink", but it would be cleaner and more consistent when new or updated data becomes available.
While I think I agree that doing it "properly" via a second series is preferable, I don't necessarily agree that making the entirety of the "future" (data, gridlines, and even the axis) semi-transparent is "poor looking". I think it could be seen as adding more emphasis to the "future-ness" of the forecast data.
In short, it's another tool for the toolbox, even if it's never needed.
Simply and clever 🙂
Quick & effective, cool. thanks.
I always use the dummy series.
Nice little trick, thanks very much!
Two sets of data better. Control is much better.
You can use the same chart next month to see what is actual and what is forecast.
To use this trick, I think grid lines has to be removed, that will make the graphic much more sharp.
to be honest, i dont understand why there is needed to do this way... in this case horizontal lines will be pale as well. then why a just can't change the color of the line partly???
Great tutorial. Thanks for the tutorial!