Today, lets learn how to make a simple timer app using Excel. First some background…,
 Recently, I learned how to solve Rubik’s cube from my nephew. As a budding cuber, I wanted to track my progress. Initially I used the stopwatch in my iPhone. But it wont let me track previous times. So I thought, “Well, I can use Excel for this”.
Recently, I learned how to solve Rubik’s cube from my nephew. As a budding cuber, I wanted to track my progress. Initially I used the stopwatch in my iPhone. But it wont let me track previous times. So I thought, “Well, I can use Excel for this”.
So I made a small timer app using Excel. Its quite minimalistic. It has a single button. I press it and it tracks the start time (date & time stamp). If I press the button again, it records the duration.
This way, I can see my progress over next few weeks and may be plot the trend.
Demo of the Excel VBA timer
Here is a short demo. This is what we will be building.
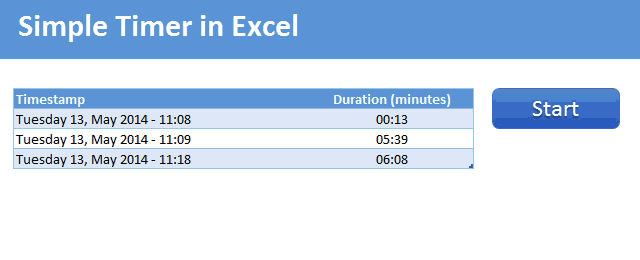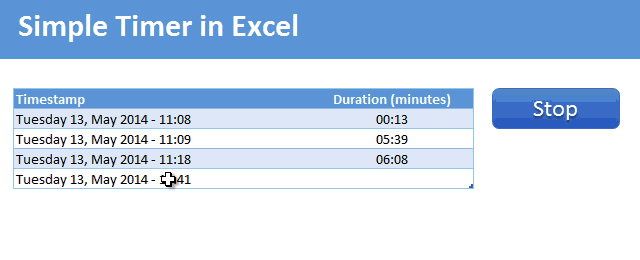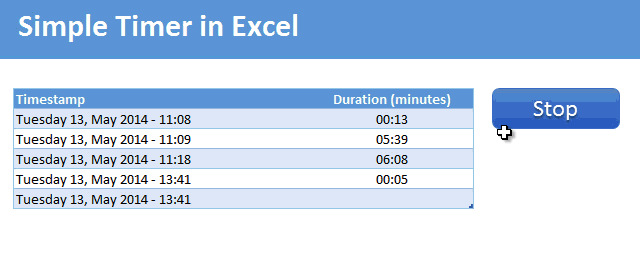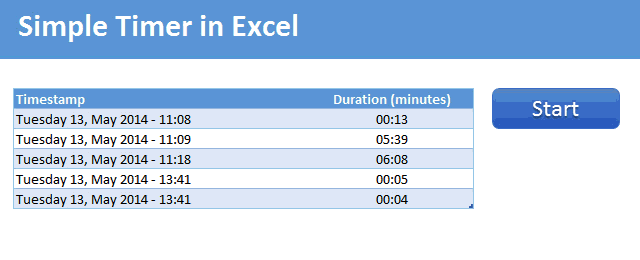
Tutorial to make a timer in Excel
To make a timer app in Excel, first we need to understand the logic for this. If VBA apps can be defined on a scale of 1 to 10 (1 being easiest to develop and 10 being most complex), our timer app can be classified as 1.5. It is really simple. But nevertheless, it is a good idea to list down various ingredients and basic logic to follow.
So we need,
- A table to store the time stamps & durations
- A button (simple text box will do) to start & stop the timer
Set up the timer worksheet
In a blank worksheet, make space for a 2 column table. Type Time stamp & Duration as column headings and make a table from these (CTRL+T to insert the table)
Note: For the macro to work, you do not need a table. Any 2 column range will do. A table makes our timer app look sexy.
Also, insert a rounded rectangle and format it to look like a button (from Format Ribbon > Shape Styles, select something slick and pretty)
In a blank cell, type the word “Start”. Name this cell as timer.button.label
Now, click on the rounded rectangle button, go to formula bar and type =timer.button.label
💡 Tip: Yes, you can assign names or cell references to shapes. This way, whatever text is in the cell will be shown inside the shape.
Other names to make:
Although we can write VBA code without creating these names, our code will be readable with these names. So here we go:
- Select the header “Timestamp” of the table and name it as time.stamp.start
- Name the table as Durations from Table Design ribbon
- In a blank cell, write the formula =COUNTA(Durations[Timestamp])
- This counts how many timestamps are already inserted.
- Now name this cell as count.of.timestamps
We are done. Lets roll in to VBA.
Writing the VBA code for timer
Open VBE (Visual Basic Editor) and insert a new module in your timer workbook. There write this code.
Sub startStopTimer()
If Range("timer.button.label") = "Start" Then
Range("time.stamp.start").Offset(Range("count.of.timestamps") + 1).Value = Now
Range("timer.button.label") = "Stop"
Else
Range("time.stamp.start").Offset(Range("count.of.timestamps"), 1).Value = Now - Range("time.stamp.start").Offset(Range("count.of.timestamps"))
Range("timer.button.label") = "Start"
End If
End Sub
Assign this macro to the timer button
Right click on timer button and choose “Assign macro”. Select the startStopTimer sub from the list and click ok.
Now go ahead and test it. Assuming you have used same names as per this post, your timer should work.
How this macro works?
When you click on the timer button, you want one of the 2 things to happen.
- You want to start the timer
- You want to stop the timer
What you want to do can be checked with this logical check.
Range("timer.button.label") = "Start"
If this is true, then you want to start the timer.
Else, you want to stop the timer.
If you want to start the timer
Then, we need to go to the last row of the table + 1 and insert current time (now) in that cell.
This is done by,
Range("time.stamp.start").Offset(Range("count.of.timestamps") + 1).Value = Now
Once we do that, we need to change timer button’s text to “Stop”.
This is done by,
Range("timer.button.label") = "Stop"
If you want to stop the timer
Then, we need to go to the last row’s 2nd column of the table and print the difference between latest time (now) and starting time (last row, first column value)
This is done by,
Range("time.stamp.start").Offset(Range("count.of.timestamps"), 1).Value = Now - Range("time.stamp.start").Offset(Range("count.of.timestamps"))
Once we do that, we need to change the button text to “Start” by using this code:
Range("timer.button.label") = "Start"
That’s all. Our VBA code is rather simple.
One last step, formatting the duration
If you look at the duration, it could read something like 0.0042354. This is because duration is displayed as a fraction of day. So 0.0042354 means the duration is 0.42% of a day.
Now, wouldn’t it be better if we can show this in minutes and seconds?
To do that, select the entire table column of durations, press CTRL+1
Then, set formatting as custom and type code as [mm]:ss
And you are done!
Download Simple Timer Excel VBA workbook
Click here to download Simple Timer Excel VBA workbook. Play with it. Use it to track your Sudoku, crossword or knitting times. Or even Rubik’s cube times. See what trends and patterns you can uncover.
Do you use Excel for tracking time?
I know many companies use Excel based trackers to keep track of employee time. I personally use time tracking features of Excel for needs like this all the time.
What about you? Do you use Excel time functions like NOW, TODAY and VBA to track progress? What techniques you apply? Please share using comments.
Like tracking? You will love these
If you track things with Excel, you are going to find below tutorials very useful.
- Tracking issues & risks – Project management
- Tracking to dos – Project Management
- Expense tracker using Excel – 7 templates
- Annual goals tracker
- Bonus: Introduction to VBA – 5 part crash course
Note: Rubik’s cube image by Booyabazooka thru Wikimedia


















One Response to “Excel Tips Submitted by You [Part 4]”
ctl+d
copy the up cell